PPT Waves, Sound and Light PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3062853

Speed at which the wave disturbance moves. Depends only on the properties of the medium. Also called the propagation speed. Transverse wave. Oscillations where particles are displaced perpendicular to the wave direction. Longitudinal wave. Oscillations where particles are displaced parallel to the wave direction.
Waves of Light and Sound Study Guide Diagram Quizlet

Nearly any type of wave can be defined as a transverse or a longitudinal wave and the ability to categorize waves into these two categories is extremely useful for energy transfer concepts. To elaborate -- consider light, which is a transverse wave. Light waves can pass through particles that have tigthly packed particles, and these particles.
Transverse vs Longitudinal Wave Leverage Edu
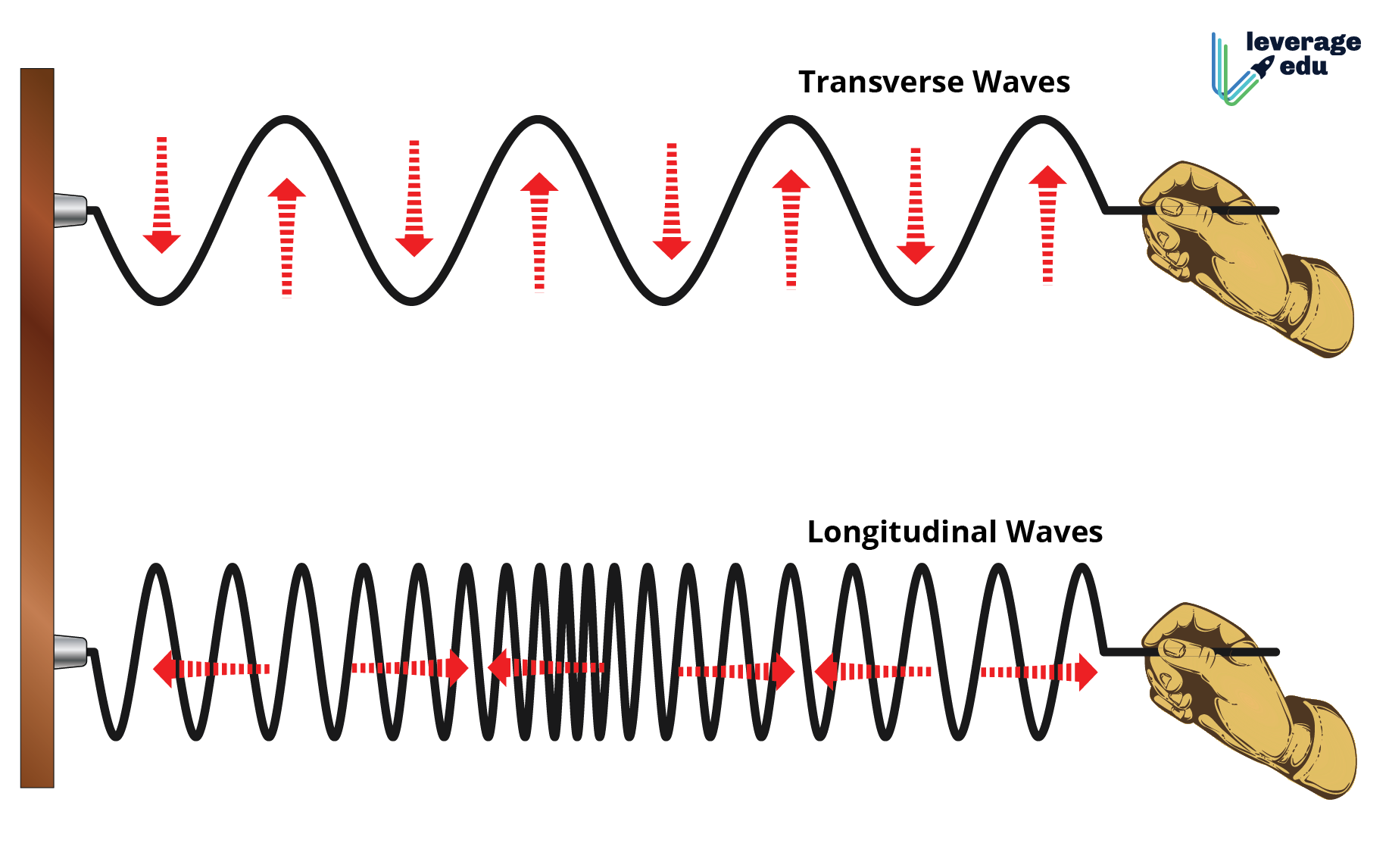
Characteristics of longitudinal and transverse waves. Google Classroom. Below is an image of a transverse wave through a medium where the dashed line is the medium's equilibrium position. What does the arrow represent? Use a coordinate system where upward is the positive direction for medium displacement.
Longitudinal and Transverse Waves Explanation, Difference Teachoo
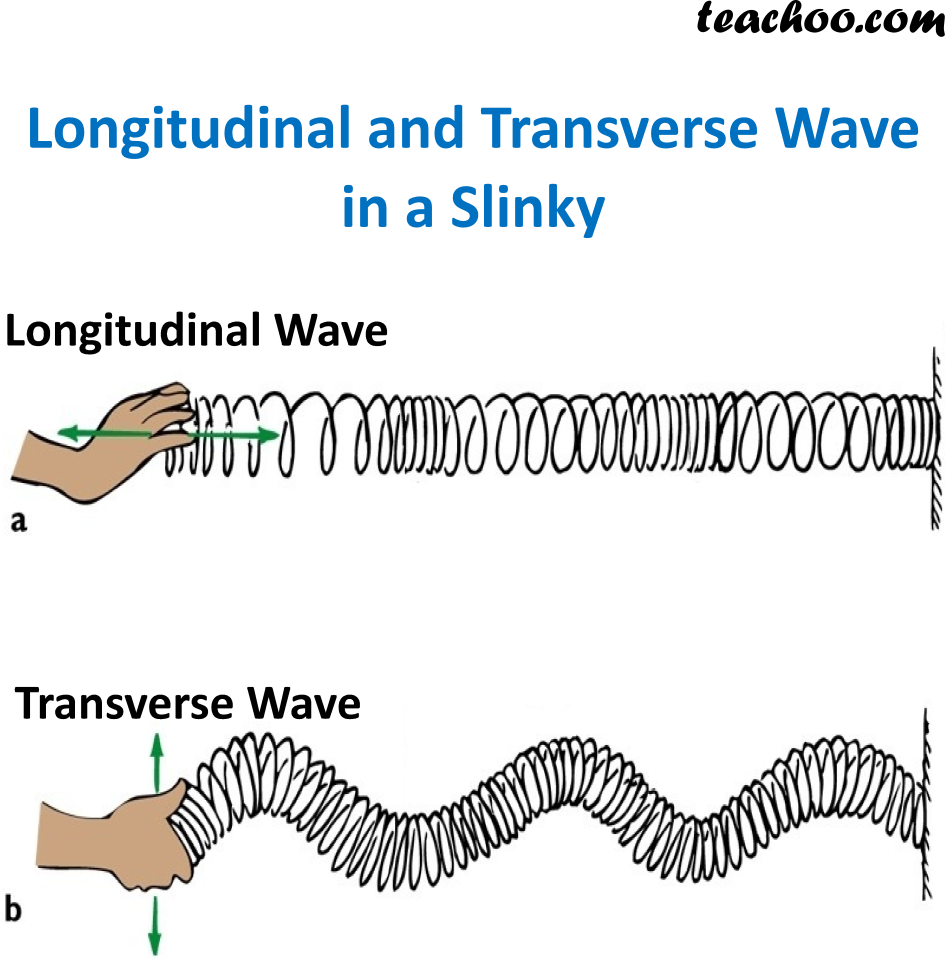
Remember, for a string wave, the string moves perpendicular to the string, while the wave travels along the string. Thus, a string wave is a transverse wave. For sound waves, the air molecules move along the motion of the wave, and hence, sound is a longitudinal wave. What is light: longitudinal or transverse?
PPT Waves PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2610536
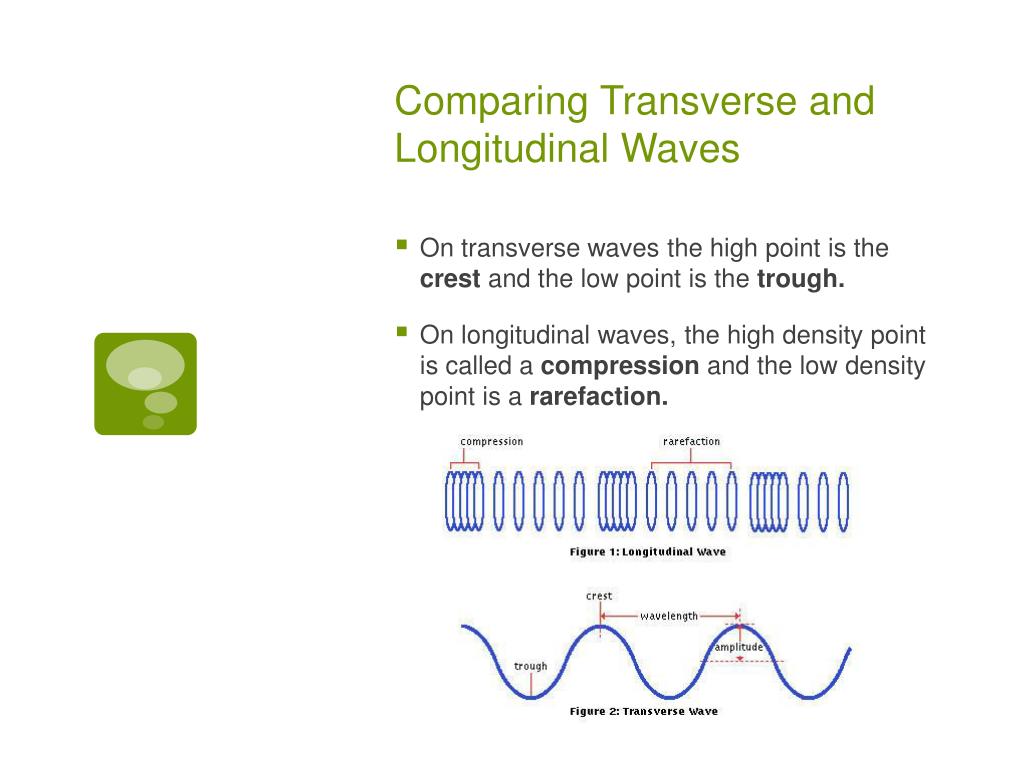
Transverse waves have peaks and troughs. The peak is the crest or top point of the wave, and the trough is the valley or bottom point of the wave. Waves produced in a string are standing waves. Light waves are electromagnetic waves, and all electromagnetic waves are an example of transverse waves. Difference between Longitudinal and Transverse.
(PPT) Transverse Longitudinal. Wave Transverse Longitudinal Eg. Sound Eg. Light A component of

Mechanical waves can be produced only in media which possess elasticity and inertia. There are three types of mechanical waves: transverse waves, longitudinal waves, and surface waves. Some of the most common examples of mechanical waves are water waves, sound waves, and seismic waves. Like all waves, mechanical waves transport energy.
wave Students Britannica Kids Homework Help

Mathematics and experiments show that light is a transverse wave - the electric and magnetic field vectors point in directions that are perpendicular to the direction of motion of the light wave (and as it turns out, they also rare always perpendicular to each other). Figure 2.1.1 - Electromagnetic Wave. The red arrows in the figure above.
Light Optical Profilometer Training
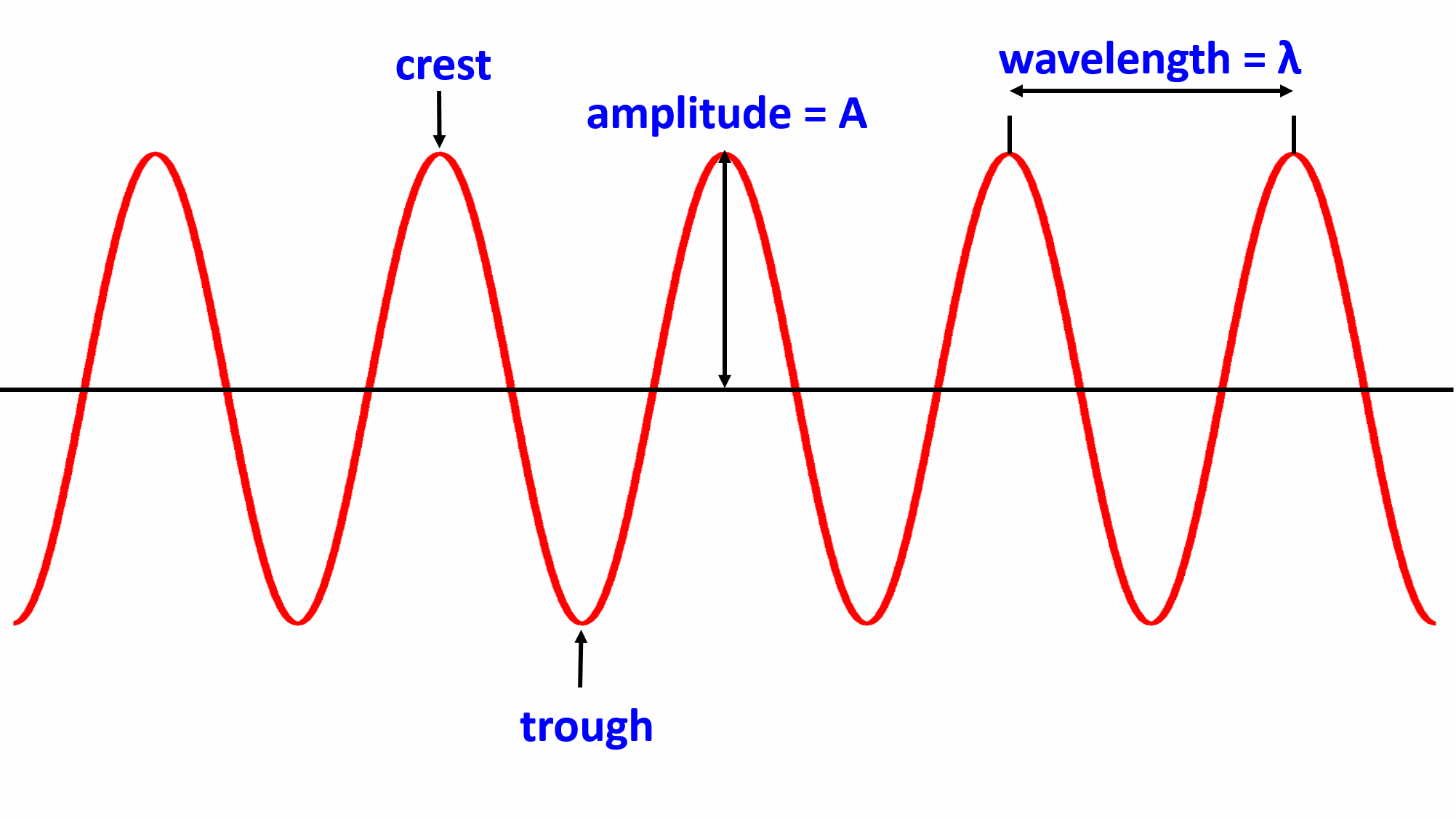
Transverse and longitudinal waves are two types of mechanical waves, which involve the transfer of energy through a medium (e.g. water, air, a solid). Learn about transverse and longitudinal waves through the examples of a shaken rope and a sound wave. Finally learn about the difference between a single wave pulse and periodic waves.
PPT General Wave Properties, the Spectrum, and Astronomy PowerPoint
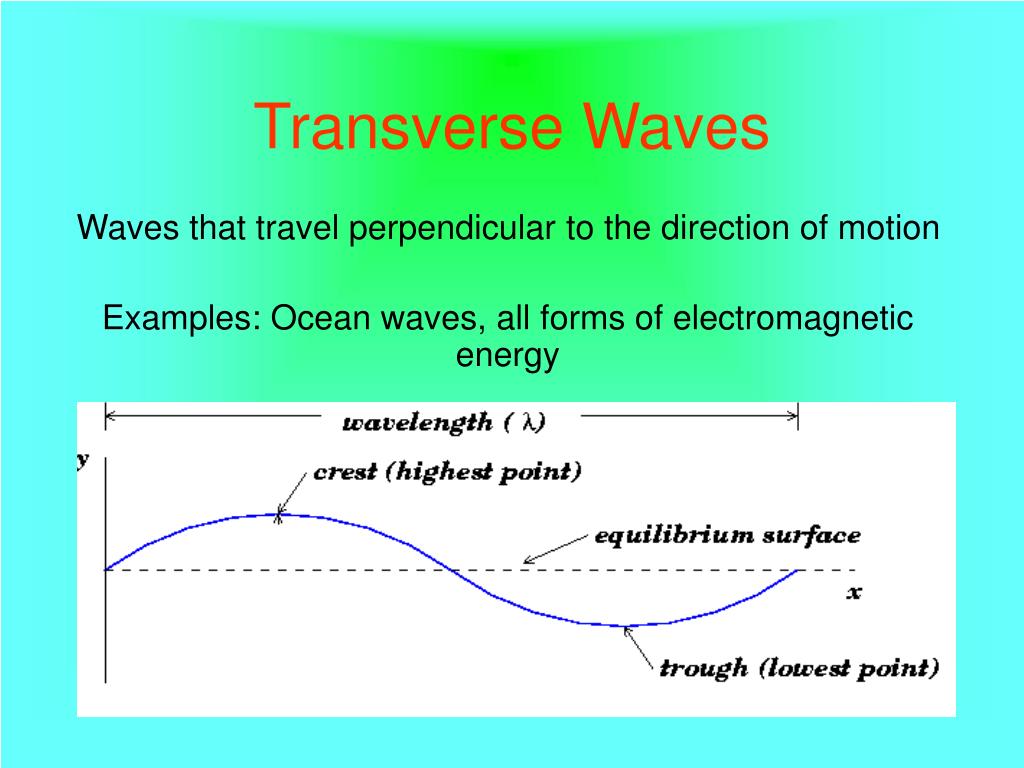
Conclusion. Light waves are an example of transverse waves, because the waves move at a 90-degree angle to the direction in which the energy is traveling. Light waves do not need a medium to transfer energy through—they can travel through vacuums, which is how we get light from the sun and the far-away stars in our universe.
Difference between Longitudinal and Transverse Wave
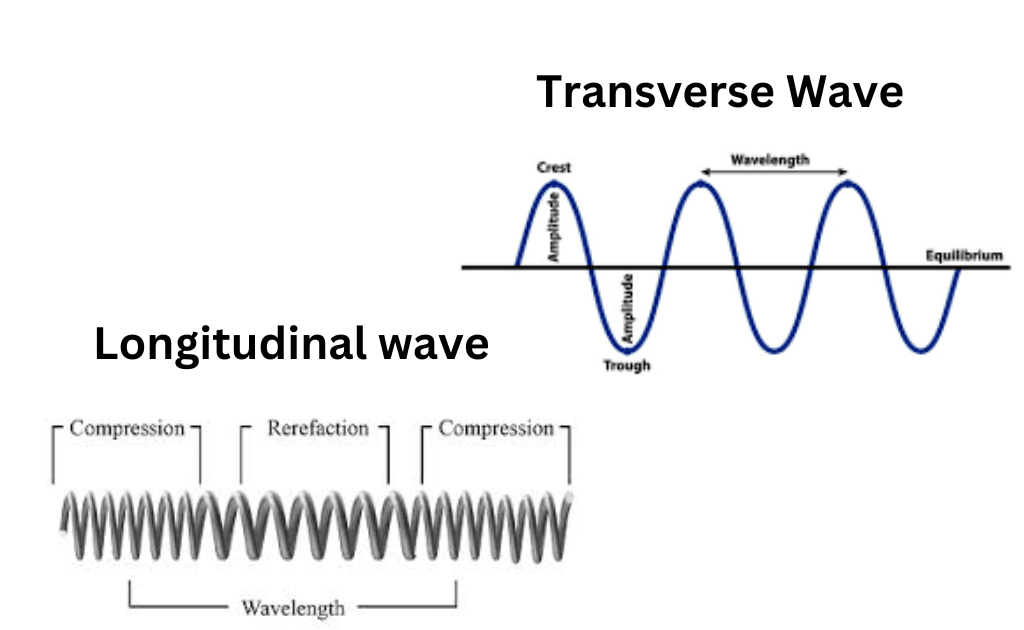
Light waves are purely transverse, while sound waves are purely longitudinal. Ocean waves are a peculiar mixture of transverse and longitudinal, with parcels of water moving in elliptical trajectories as waves pass. Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation. The undulations in an electromagnetic wave occur in the electric and magnetic fields.
Are Light Waves Transverse or Longitudinal? The Interesting Answer! Optics Mag

transverse wave, motion in which all points on a wave oscillate along paths at right angles to the direction of the wave's advance. Surface ripples on water, seismic S (secondary) waves, and electromagnetic ( e.g., radio and light) waves are examples of transverse waves. A simple transverse wave can be represented by a sine or cosine curve.
Properties of waves and wave cycles. Scalar, transverse, energy and more. Chris Plouffe

Distinguish a longitudinal wave from a transverse wave and give examples of such waves; Teacher Support.. such as visible light. Sound waves in air and water are longitudinal. Their disturbances are periodic variations in pressure that are transmitted in fluids. Figure 13.5 The wave on a guitar string is transverse. However, the sound wave.
2.3 Light and Optics Part 1 Spectrum, Properties of Light Introduction to

Transverse waves are contrasted with longitudinal waves, where the oscillations occur in the direction of the wave. The standard example of a longitudinal wave is a sound wave or "pressure wave" in gases, liquids, or solids, whose oscillations cause compression and expansion of the material through which the wave is propagating. Pressure waves.
Waves Part 1
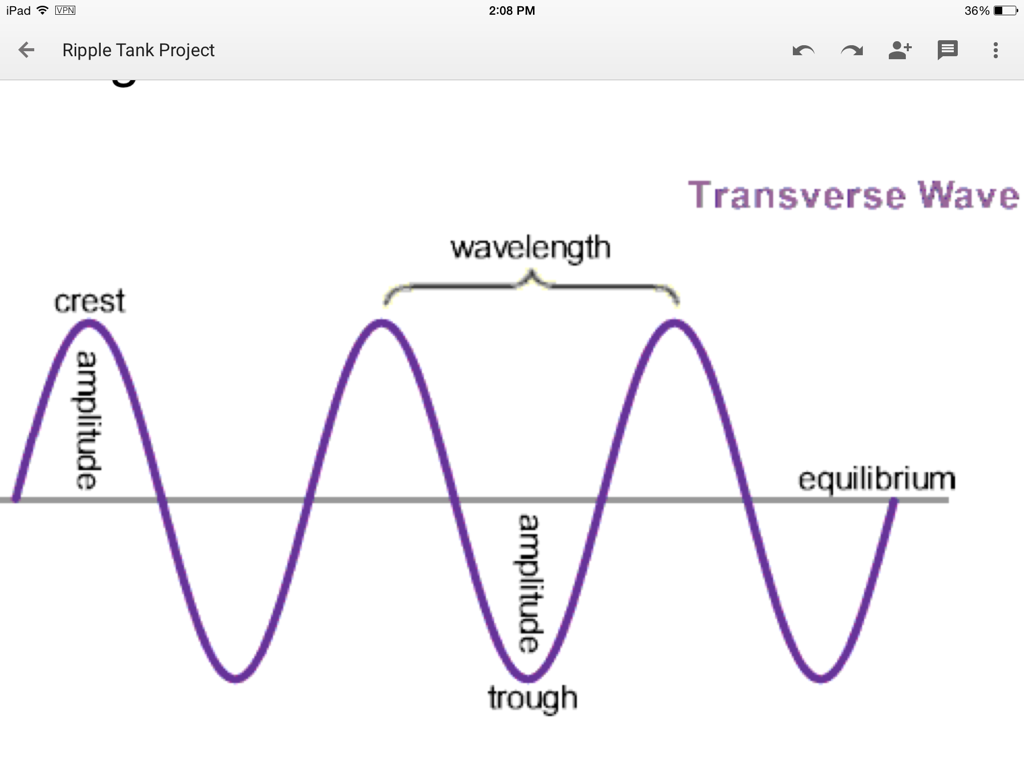
About the Author. Waves can be divided into two main types: transverse and longitudinal. Transverse waves oscillate perpendicular to the direction of travel; longitudinal waves oscillate parallel to it. There are many examples of each in every day life and some media, like earth and water, can experience both.
PPT Characteristics of Light PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2664100
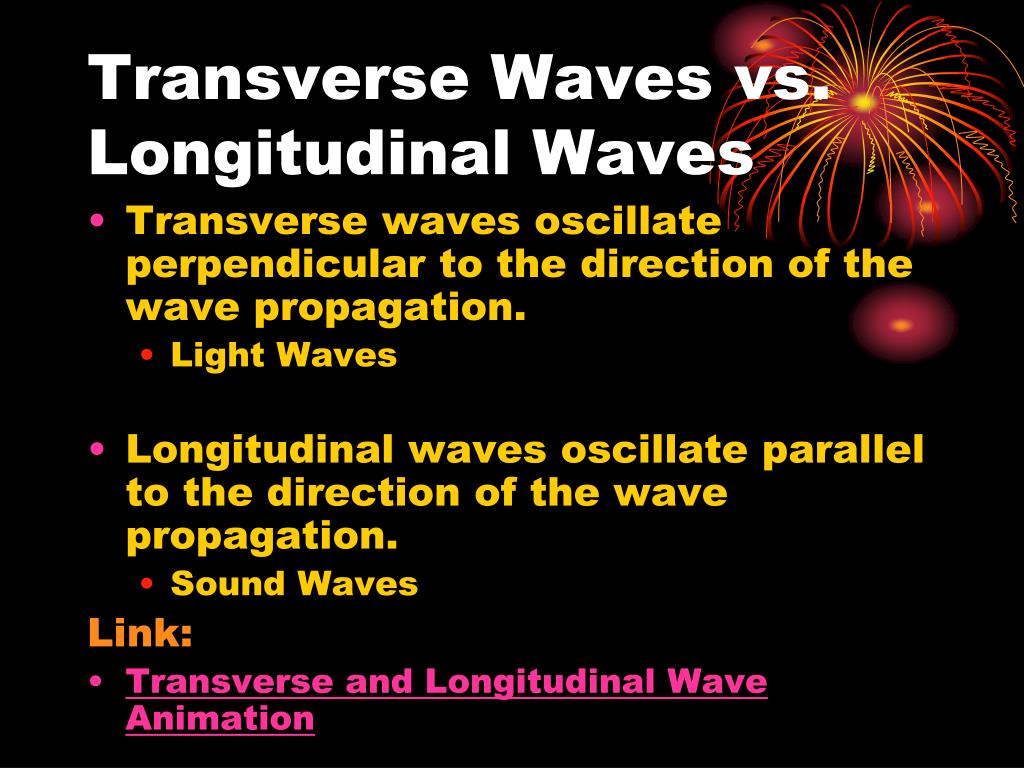
A wave can be transverse or longitudinal depending on the direction of its oscillation. Transverse waves occur when a disturbance causes oscillations perpendicular (at right angles) to the propagation (the direction of energy transfer). Longitudinal waves occur when the oscillations are parallel to the direction of propagation.. Light is an.
Wave Definitions The Science and Maths Zone

Electromagnetic fields in light waves are mainly transverse to propagation direction but actually also have longitudinal components, which may give rise to unexpected optical phenomena involving.
.